Gene Therapy Market Projected to Reach USD 27,250.20 Million by 2034, Growing at a CAGR of 27.1%
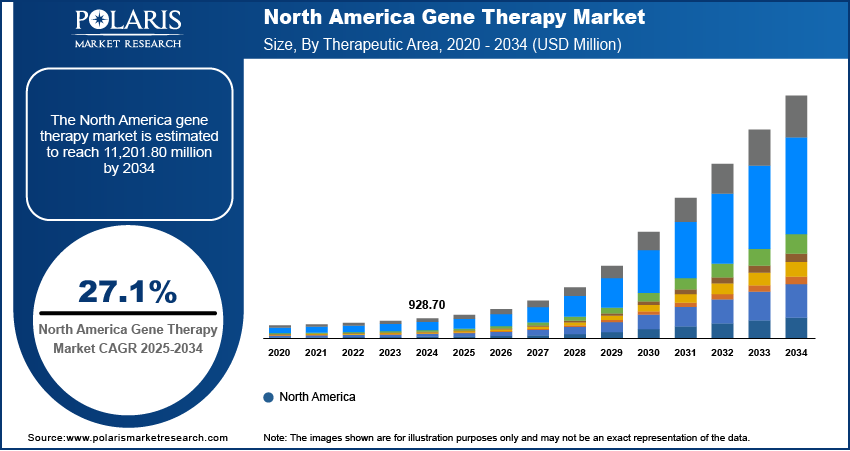
The global gene therapy market was valued at USD 2,251.50 million in 2024 and is expected to grow from USD 2,657.00 million in 2025 to USD 27,250.20 million by 2034, registering a robust CAGR of 27.1% during the forecast period (2025–2034). Gene therapy is a cutting-edge medical approach that involves altering or replacing faulty genes within a patient’s cells to treat or prevent various diseases, offering the potential for long-term or even permanent cures.
Key Market Trends & Insights:
- Rise in Rare Disease Treatments: Gene therapy is increasingly used to target rare genetic disorders, offering potential cures where traditional treatments fall short.
- Advancements in Vector Technology: Innovations in viral and non-viral vectors are improving the safety, precision, and delivery of gene therapies.
- Growing Pipeline and FDA Approvals: A surge in clinical trials and regulatory approvals is accelerating the commercialization of gene therapy products.
- Strategic Collaborations and Investments: Major pharmaceutical companies are investing in biotech startups and forming partnerships to expand their gene therapy portfolios.
Market Size & Forecast
Market Size Value in 2025: USD 2,657.00 million
Revenue Forecast by 2034: USD 27,250.20 million
CAGR: 27.1% from 2025 to 2034
Market Overview
The gene therapy market is rapidly transforming the landscape of modern medicine by offering innovative solutions for the treatment of genetic and chronic diseases. By introducing, removing, or altering genetic material within a patient’s cells, gene therapy targets the root cause of illnesses rather than just managing symptoms. This groundbreaking approach has shown significant promise in treating conditions such as certain cancers, inherited genetic disorders, and rare diseases. As scientific understanding and technological capabilities continue to advance, gene therapy is emerging as a powerful tool with the potential to deliver long-lasting or even curative effects.
The market is being propelled by advancements in molecular biology, increased investment in biotech research, and rising demand for personalized medicine. A growing number of clinical trials, combined with favorable regulatory support and faster approval pathways, are helping bring gene therapies to market more quickly. At the same time, strategic collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are enhancing innovation. As awareness increases and treatment outcomes improve, gene therapy is expected to play a pivotal role in the future of healthcare.
Request for Free Sample:
https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/gene-therapy-market/request-for-sample
Key Market Growth Drivers:
- Advancements in Genetic Engineering: Innovations in CRISPR, viral vectors, and genome editing are enhancing the safety and efficacy of gene therapies.
- Rising Prevalence of Genetic Disorders: Increasing cases of rare and inherited diseases are boosting demand for curative treatment options.
- Growing Investment in Biotech R&D: Substantial funding from governments and private sectors is accelerating research and development in gene therapy.
- Favorable Regulatory Environment: Expedited approval pathways and support from regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA are promoting faster market entry.
- Increased Focus on Personalized Medicine: Gene therapy aligns with the trend toward customized treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles.
- Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships: Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and academic institutions are driving innovation and commercialization.
Market Challenges:
- High Treatment Costs: Gene therapy procedures remain expensive, limiting accessibility for patients and straining healthcare budgets.
- Complex Manufacturing Processes: Production of gene therapies involves intricate procedures and strict quality control, posing scalability issues.
- Regulatory and Ethical Concerns: Ongoing debates around genetic modification and long-term safety raise regulatory and public acceptance challenges.
- Limited Infrastructure in Developing Regions: Inadequate healthcare systems and lack of advanced facilities hinder adoption in low- and middle-income countries.
- Uncertain Long-Term Effects: Limited long-term data on efficacy and side effects may affect trust and widespread adoption.