Polyester Polyol From Bio-Succinic Acid growing at a CAGR of 14.9% from 2025 to 2033
Polyester Polyol From Bio-Succinic Acid Market Summary
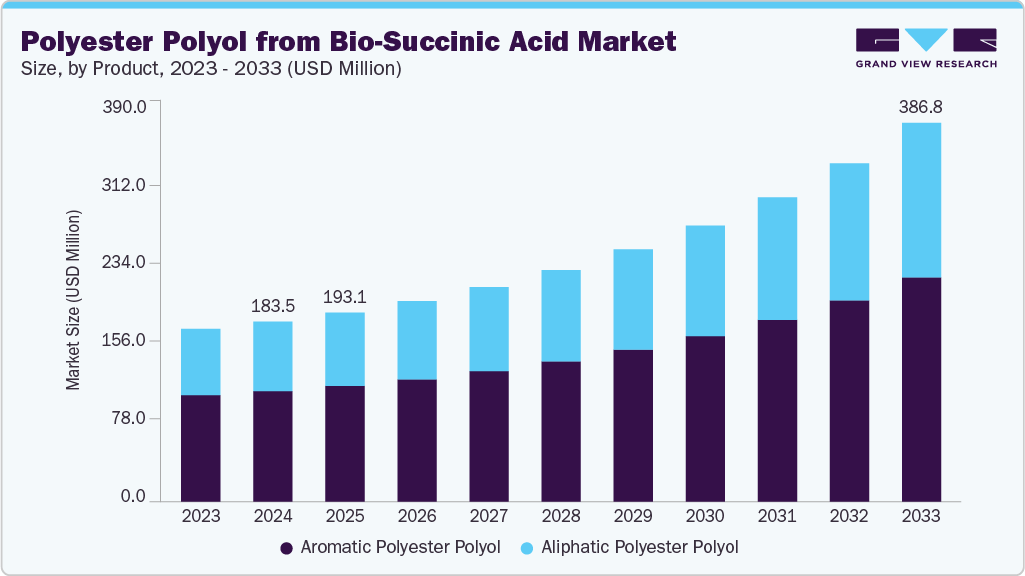
The global polyester polyol from bio-succinic acid market size was estimated at USD 183.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 386.8 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 14.9% from 2025 to 2033. The growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials across various industries.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- Asia Pacific dominated the global polyester polyol from bio-succinic acid market with the largest revenue share of 38.5% in 2024.
- The polyester polyol from bio-succinic acid market in U.S. is expected to grow at a substantial CAGR from 2025 to 2033.
- By product, the aromatic polyester polyol segment held the highest market share of 61.4% in 2024 in terms of revenue.
- By application, the polyurethane segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 15% from 2025 to 2033 in terms of revenue.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 183.5 Million
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 386.8 Million
- CAGR (2025-2033): 14.9%
- Asia Pacific: Largest market in 2024
Request Free Sample Report: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/polyester-polyol-bio-succinic-acid-market-report/request/rs1
The shift toward renewable feedstocks, such as bio-succinic acid, aligns with global initiatives to reduce carbon footprints and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, advancements in biotechnological processes have enhanced the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of producing bio-based polyols, further accelerating market adoption. The increasing emphasis on sustainability and the use of bio-based raw materials is accelerating the shift toward renewable intermediates in the production of polyurethanes. Linear polyester polyols made entirely from renewable sources can be synthesized with bio-succinic acid, bio-sebacic acid, bio-1,3-propane diol, and bio-1,4-butane diol. Succinic acid, which is generated through the fermentation of sugars derived from corn, acts as a crucial aliphatic diacid in the polyol structure, delivering enhanced performance and environmental advantages. These bio-derived polyester polyols are particularly suitable for creating polyurethane elastomers, especially when bio-1,4-butanediol is used as a chain extender.
One of the major restraints hindering the widespread adoption of bio-succinic acid-based polyester polyols is their technical and performance limitations, particularly in demanding polyurethane applications. These polyols often exhibit inferior mechanical and thermal properties, especially in rigid applications such as insulation foams and structural components. According to a study published in Polymer Testing (2020) have shown that rigid foams made from succinic acid-derived polyols can display 10-15% lower compressive strength compared to traditional aromatic polyester polyols derived from phthalic anhydride, limiting their suitability for high-load or thermally intense environments.
According to the Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on Industrial Emissions (recast), commonly known as the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), serves as a foundational regulatory framework to minimize the environmental impact of industrial activities across the European Union. It integrates and streamlines seven earlier directives, including the Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control (IPPC) Directive, to ensure high protection for human health and the environment.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The industry is moderately concentrated, with a combination of well-established chemical manufacturers and innovative startups focusing on bio-based solutions. Leading companies, including BASF, Covestro, and Succinity, are investing heavily in research and development to improve the performance, sustainability, and versatility of bio-based polyester polyols. These players leverage advanced biotechnological processes to optimize bio-succinic acid production, ensuring consistent quality and compatibility with polyurethane applications.
Emerging players are differentiating themselves by focusing on niche applications, small-batch production, and eco-certified offerings that appeal to sustainability-conscious manufacturers. The market is witnessing gradual consolidation, as larger firms acquire or partner with smaller innovators to expand their product portfolios and technological capabilities. Additionally, the emphasis on regulatory compliance and environmental standards is shaping production practices, pushing the market toward renewable feedstocks, reduced carbon emissions, and circular economy principles.
Polyester Polyol From Bio-Succinic Acid Market Report Scope
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 193.1 million |
|
Revenue forecast in 2033 |
USD 386.8 million |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 14.9% from 2025 to 2033 |
|
Base year for estimation |
2024 |
|
Historical data |
2018 – 2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2025 – 2033 |
|
Quantitative units |
Volume in kilotons; revenue in USD million/billion, and CAGR from 2025 to 2033 |
|
Report coverage |
Volume & revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Segments covered |
Product, application, region |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; France; Italy; Spain; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Saudi Arabia; Brazil; Argentina |
|
Key companies profiled |
Alfa Chemicals; Arkema; Synthesia Technology Group; BASF SE; DIC CORPORATION; Dow; Evonik Industries AG; Huntsman Corporation; Gantrade Corporation; Purinova Sp. z o.o.; Stepan Company; Oleon NV. |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analyst’s working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional, and segment scope. |
|
Pricing and purchase options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |