Oral Clinical Nutrition Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis growing at a CAGR of 5.0% from 2025 to 2030
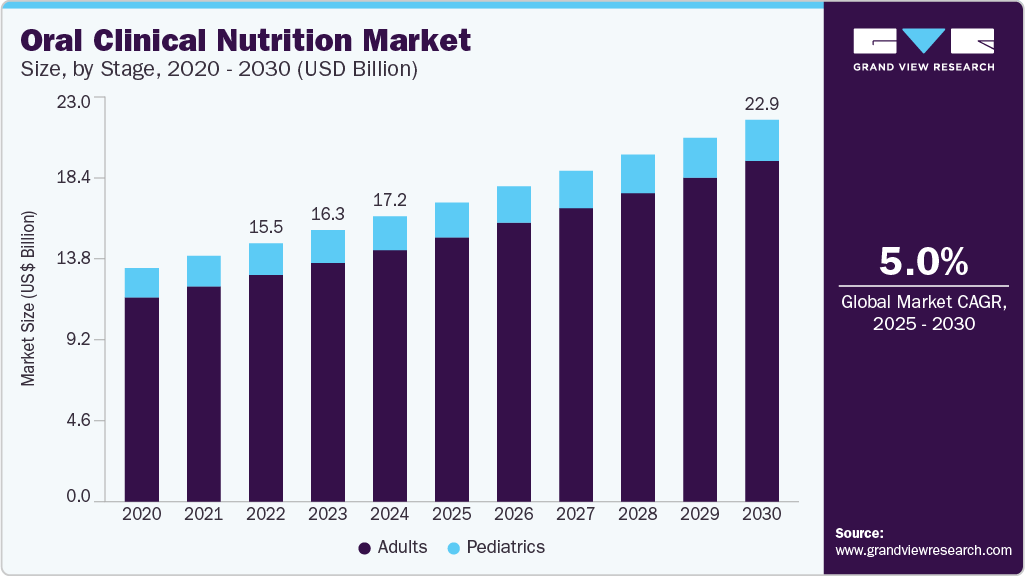
The global oral clinical nutrition market size was estimated at USD 17.16 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.0% from 2025 to 2030. The growing rates of malnutrition in adults, along with increasing cases of obesity and chronic conditions such as cancer and diabetes, are key drivers of market growth.
Key Highlights:
- North America dominated the oral clinical nutrition market with the largest revenue share of 30.50% in 2024.
- The oral clinical nutrition market in the U.S. accounted for the largest share in North America in 2024.
- By stage, the adult segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 88.15% in 2024.
- By indication, the cancer care segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024.
- By sales channel, the institutional sales segment accounted for the largest share in 2024.
Request a free sample copy or view report summary: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/oral-clinical-nutrition-market-report/request/rs1
Oral clinical nutrition products in powder, liquid, and semi-solid forms deliver essential nutrients such as vitamins, proteins, and carbohydrates. Manufacturers are introducing new flavors to improve taste and attract more consumers, increasing sales and market demand. For instance, in May 2023, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Factory released an updated ENORAS Liquid, now available in coffee and tea flavors. This specialized liquid is designed for both feeding tube and oral administration, offering more palatable options for patients.
According to WHO, the global population aged 60 & above significantly increased from around 1 billion in 2020 to about 1.4 billion in 2030 and is expected to almost double by 2050 to reach around 2.1 billion. The number of elderly patients with critical illnesses has significantly increased in the past few years. The risk of malnutrition and frailty among the geriatric population with comorbidities, such as stroke, depression, and dementia, is much higher, mainly owing to various age-related changes in body composition and muscle mass. This results in a reduced ability to perform Activities of Daily Living (ADLs), thereby increasing the risk of falls or injuries. Therefore, it is important to analyze the pathophysiology behind the condition (nutritional deficiency).