Industrial Cyber Security Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis growing at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2025 to 2033
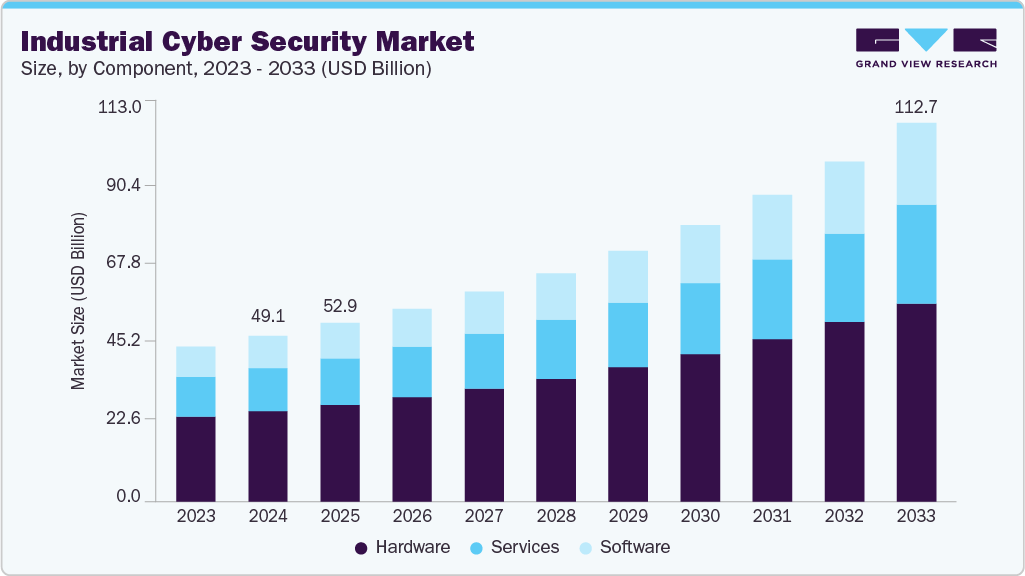
The global industrial cyber security market size was estimated at USD 49.13 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 112.66 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2025 to 2033. The growing convergence of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) systems across critical infrastructure and manufacturing environments is driving the growth of the industrial cyber security industry.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- North America held a 36.5% revenue share of the global industrial cyber security market in 2024.
- In the U.S., the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting industrial operations is accelerating the demand for industrial cyber security systems.
- By component, the hardware segment held the largest revenue share of 54.9% in 2024.
- By solution type, the SCADA segment held the largest revenue share in 2024.
- By security type, the infrastructure protection segment held the largest revenue share in 2024.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 49.13 Billion
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 112.66 Billion
- CAGR (2025-2033): 9.9%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
- Asia Pacific: Fastest-growing market
Request a free sample copy or view report summary: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/industrial-cyber-security-market-report/request/rs1
The rising adoption of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices and cloud-based platforms is driving the industrial cyber security market growth. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, but they also introduce complex cybersecurity challenges due to the sheer volume of devices and the necessity for secure data transmission. Industrial organizations are responding by integrating cybersecurity at both the network and device levels, driving demand for solutions that offer device authentication, encrypted communication, and anomaly detection powered by AI and machine learning. Moreover, the growing reliance on third-party vendors and remote access for managing OT infrastructure makes it essential to deploy identity and access management (IAM) systems, secure remote connectivity, and zero-trust architectures, further boosting the market.
The growth of digital twins, predictive maintenance, and advanced analytics in industrial settings is further intensifying the need for sophisticated cybersecurity frameworks. These technologies depend on the seamless flow of real-time data across machines, sensors, cloud platforms, and analytics engines. Any interruption, manipulation, or unauthorized access to this data degrades operational efficiency and poses significant risks to safety and asset integrity. Consequently, companies are deploying end-to-end encryption, secure APIs, and network segmentation techniques to ensure data authenticity and integrity in highly digitized industrial workflows. This shift is especially evident in high-stakes sectors such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and energy production, where even brief system failures can result in millions of dollars in losses or regulatory violations.
The trend toward decentralized industrial operations enabled by mobile, edge computing, and 5G connectivity is also transforming cybersecurity needs. With more devices and control systems being deployed at the edge of networks rather than centralized locations, the potential entry points for cyber threats have multiplied. Traditional perimeter-based security is no longer sufficient, and as a result, zero-trust architectures and secure edge computing frameworks are being adopted to protect dispersed assets. These architectures assume every user, device, or system is untrusted by default and must continuously validate identity and security posture before accessing industrial networks. This model is proving vital for companies managing remote facilities, such as wind farms, offshore rigs, or mining sites, where physical oversight is limited.
Furthermore, the expansion of smart factories and Industry 4.0 initiatives across various sectors is contributing to the growth of the industrial cybersecurity industry. Smart factories rely on interconnected sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotics, and AI-driven decision-making systems to enable predictive maintenance, automated workflows, and quality assurance. However, these highly automated environments are also attractive targets for cyber attackers due to their complexity and reliance on real-time data. A breach in these ecosystems can halt operations and lead to significant productivity losses. To address these vulnerabilities, manufacturers are embedding cybersecurity into the design phase of smart factory infrastructure, deploying anomaly detection, identity management solutions, and real-time monitoring systems that can rapidly isolate threats without shutting down production.