Green Ammonia Market projected to reach USD 48,983.77 million by 2034, growing at a robust CAGR of 63.80%
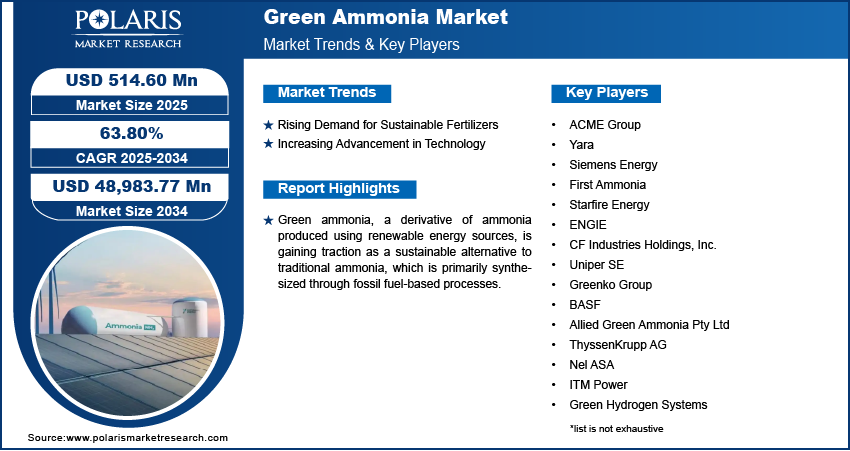
The global Green Ammonia Market was valued at USD 314.22 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 63.80% from 2025 to 2034. The push toward carbon-neutral industrial feedstocks and renewable energy storage solutions is transforming green ammonia into a key growth segment.
Market Trends & Insights
- Hydrogen Economy Synergy: The market is benefiting from the accelerating development of the hydrogen economy. Green ammonia is emerging as a key hydrogen carrier due to its higher energy density and ease of storage and transportation.
- Maritime Fuel Alternative: Regulatory pressure to reduce maritime emissions is propelling green ammonia as a sustainable marine fuel, especially for long-distance shipping.
- Ammonia as an Energy Storage Medium: With intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind, green ammonia offers a practical storage solution that can be reconverted into electricity or used directly as fuel.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in ammonia synthesis and storage infrastructure are increasing, especially near renewable power generation facilities.
- Policy Support and Incentives: Governmental initiatives, subsidies, and carbon credit frameworks in Europe, Asia-Pacific, and North America are fostering market growth by reducing production costs and enhancing adoption.
Market Size & Forecast
Market size value in 2025 USD – 514.60 Million
Revenue forecast in 2034 USD – 48983.77 Million
CAGR – 63.80% from 2025 – 2034
Request for Free Sample:
https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/green-ammonia-market/request-for-sample
Market Overview
The global green ammonia market is poised for rapid expansion, driven by the rising demand for sustainable and carbon-free energy solutions. Green ammonia is synthesized using renewable energy sources through water electrolysis and nitrogen separation, offering a zero-carbon alternative to conventional ammonia production. It holds immense potential across sectors like agriculture, energy, and transportation due to its versatility as both a fertilizer and clean fuel. As governments and industries increasingly pursue decarbonization targets, green ammonia is gaining attention as a promising vector for hydrogen storage and transportation. The market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, especially in regions focused on renewable energy integration and clean fuel adoption.
Market Growth Drivers
- Decarbonization Goals: Stricter global climate policies and net-zero carbon targets are accelerating the shift from grey to green ammonia.
- Expanding Renewable Energy Capacity: The declining cost of solar and wind power enhances the feasibility of green hydrogen and ammonia production.
- Rising Demand for Green Fertilizers: Agricultural sectors are increasingly seeking eco-friendly fertilizers to reduce carbon footprints and promote sustainable farming.
- Adoption in Power Generation: Green ammonia is being explored as a co-firing fuel in thermal power plants to reduce emissions without major infrastructure overhaul.
- Strategic Global Collaborations: Countries with abundant renewable resources are entering export partnerships, driving cross-border development of green ammonia value chains.
Market Challenges
- High Production Costs: Compared to conventional ammonia, green ammonia remains significantly more expensive due to the cost of electrolysis and renewable electricity.
- Technological Barriers: Electrolyzer efficiency, nitrogen separation methods, and scalability remain technological hurdles that need further R&D.
- Storage and Handling Risks: Ammonia is toxic and corrosive, necessitating stringent safety standards and infrastructure investment.
- Lack of Standardized Regulations: The absence of uniform global standards for green ammonia certification and trade complicates its marketability.
- Limited End-Use Market Readiness: Despite interest, the transition of industries—especially in shipping and power—from fossil fuels to green ammonia is still in early stages and faces infrastructure and regulatory gaps.