Antifungal Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis growing at a CAGR of 3.9% from 2025 to 2030
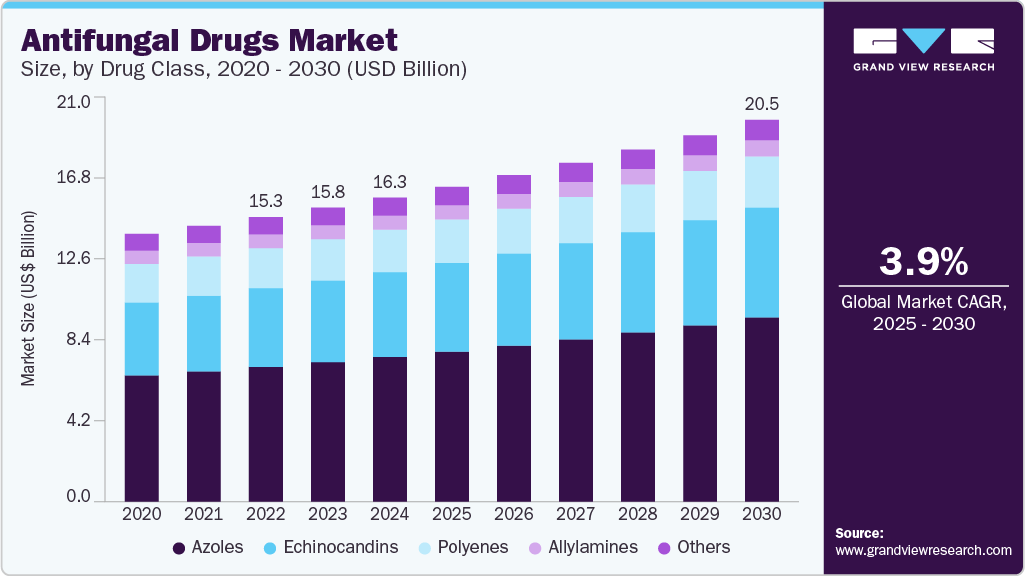
The global antifungal drugs market size was estimated at USD 16,345.9 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 20,517.1 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.9% from 2025 to 2030. The rising incidence of fungal infections, including aspergillosis and candidiasis, continues to drive market expansion amid heightened awareness following recent global health alerts.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- In terms of region, North America was the largest revenue generating market in 2023.
- Country-wise, Spain is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2024 to 2030.
- In terms of segment, azoles accounted for a revenue of USD 7,524.1 million in 2023.
- Echinocandins is the most lucrative drug class segment registering the fastest growth during the forecast period.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 16,345.9 Million
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 20,517.1 Million
- CAGR (2025-2030): 3.9%
- North America: Largest market in 2023
Key Highlights:
- North America dominates the antifungal drugs market with a share of 40.62% in 2024
- The U.S. holds a significant share within North America, driven by a high incidence of dermatophytosis and candidiasis infections
- By drug class, the azoles drug class segment dominated the market and accounted for a revenue share of 47.57% in 2024
- By indication, the candidiasis segment held the largest market share in 2024
- By dosage form, the oral drug dosage form led the market in 2024 due to its effectiveness in treating systemic infections like thrush, such as throat and mouth yeast infections
Request a free sample copy or view report summary: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/antifungal-drugs-market/request/rs1
Fungal infections range from superficial conditions affecting the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes to more severe systemic cases. The demand for broad-spectrum antifungal products with potent fungicidal activity is increasing, especially in treating infections such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and invasive fungal diseases like fungal meningitis.
Fungal diseases remain a major global health concern, particularly for individuals with weakened immune systems such as those living with HIV/AIDS. Cryptococcal meningitis, a severe fungal infection of the brain, continues to cause high mortality, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, where HIV prevalence is substantial. According to recent data, approximately 152,000 new cases of cryptococcal meningitis occur annually, resulting in around 112,000 deaths, with nearly two-thirds reported from sub-Saharan Africa. Delayed diagnosis and limited access to potent antifungal drugs significantly contribute to these outcomes, indicating a critical unmet need for stronger, more accessible treatments. Improved screening protocols for high-risk individuals, particularly those with low CD4 counts, have been emphasized to address this issue. This highlights the urgent demand for targeted interventions and enhanced global health infrastructure to combat opportunistic fungal infections.